
This page last revised 02 September 2006 -- S.M.Gon III
Introduction
Ecoregion
Conservation Targets
Viability
Goals
Portfolio
TNC Action Sites
Threats
Strategies
▫
Tables
Maps & Figures
CPT Database
Appendices
Glossary
Sources
.

The viney legume nuku'i'iwi (Strongylodon ruber) grows in mesic forest on several islands.


Lowland Mesic System
Natural communities below1,000 m (ca 3,000 ft) elevation, receiving bewteen 50 and 75inches annual precipitation, or otherwise bearing prevailingly mesicsubstrate conditions comprise the lowland mesic system in theHawaiian High Islands Ecoregion. This system is found on theislands of Hawai‘i, Maui, Moloka‘i, Lāna‘i,O‘ahu, and Kaua‘i, and may be found on both windward andleeward sides of the islands, for example, the Kona flankof Mauna Loa, the leeward flank of West Maui, the leewardside of East Moloka‘i, the slopes surrounding the summit ofLāna‘ihale (Lāna‘i), the lower slopes of theWai‘anae Mountains (O‘ahu) and the leeward slopes of theKo‘olau Mountains (O‘ahu), and the western slopes ofKaua‘i. It occurs typically below either the lowland wet system or the montane mesic system, and above the lowland dry system.There are a number of naturalcommunities described within this system, including a variety ofgrasslands, shrublands, and forests. Biologicaldiversity is high in this system, which is noted in particular fortree species diversity. A number of specialized plants and animalsoccur there, such as the Hawaiianbat, ‘Ōpe‘ape‘a ( Lasiurus cinereus semotus) and the native vine nuku‘i‘iwi (Strongylodon ruber). This system is of secondary importance for the forest bird concentration.

The Hawaiian bat, 'ōpe'ape'a, maintains highest densities in lowland mesic forest on all of the main islands.
Natural communities and species of this system are listed among nested targets via the appendices.

The distribution of the Lowland Mesic System across the Hawaiian High Islands Ecoregion is depicted below:
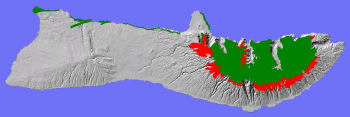
The Lowland Mesic System on Moloka'i (red above) typically occurs at mid-flank on the leeward slopes. It is threatened by feral ungulates and wildfires.
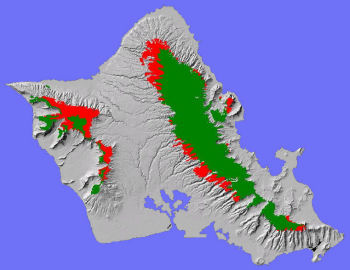
The Lowland Mesic System on O'ahu (red above) occurs in both Ko'olau (east) and Wai'anae (west) conservationareas, typically as remnant occurrences adjacent to agricultural andother developed lands.
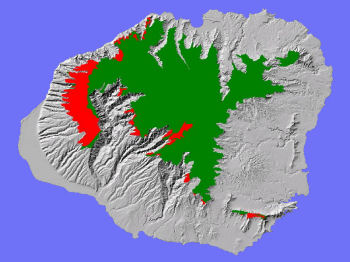
The Lowland Mesic System on Kaua'i (red above) is restricted to the leeward (western) slopes of the island.


Natural communities and species of this system are listed among nested targets via the appendices.

The distribution of the Lowland Mesic System across the Hawaiian High Islands Ecoregion is depicted below:




TheLowland Mesic System in Hawai‘i includes some of the most diverseforest communities in the ecoregion, and is a hotspot for endangeredspecies recovery and restoration efforts. Above: Diverse mesic forestin the Wai'anae conservation area, O'ahu.


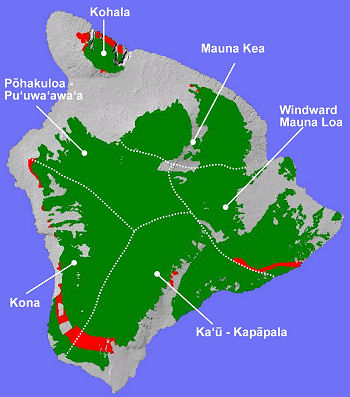
The Lowland MesicSystem on Hawai‘i Island (red areas above) occurs in all sixconservation areas, but is often reduced to remnant occurrences.
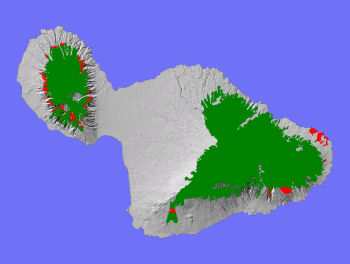
TheLowland Mesic System on Maui (red above) occurs in both East Mauiand West Maui conservation areas, typically as remnant occurrencesadjacent to agricultural and other developed lands.
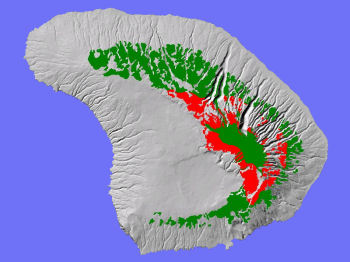
TheLowland Mesic System on Lāna'i (red above) has been greatly degradedand fragmented by feral animals (especially deer).